Overview
- Project funded by Maharashtra Pollution Control Board and Bloomberg Philanthropies.
- Project duration- June 2020 to May 2021
Description
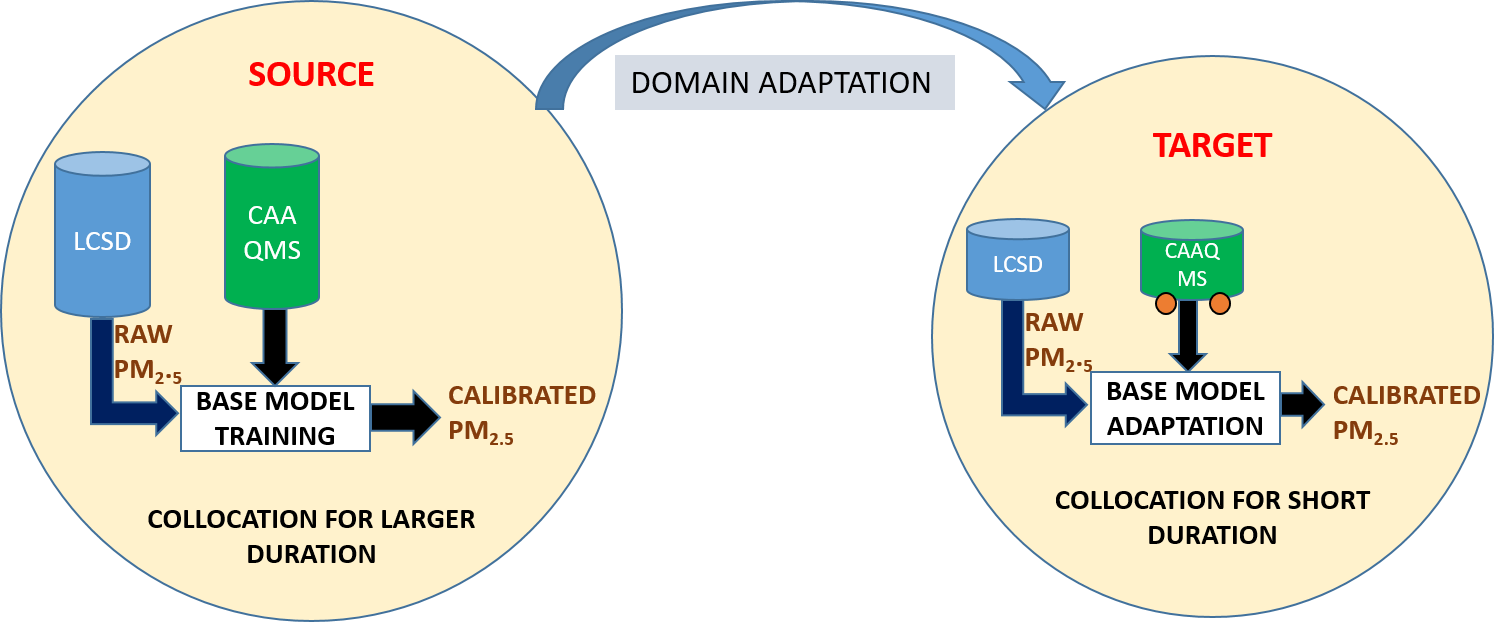
Measuring Air Quality in urban areas is necessary for public health. CAAQMS setups provide high precision measurements but are very costly. To make dense networks of air quality sensors, we need low cost sensors. Such sensors do exist but have low fidelity. We are developing machine learning based methods to calibrate the measurements of low cost sensors (LCS) to have high fidelity.
One of the major challenge here is obtaining the training data by deploying a LCS co-located with CAAQMS. There are variations in the performance of LCS devices due to their own characteristics. We designed transfer learning based adaptation of calibration models to quickly calibrate the LCS devices.
The proposed models help in reducing the collocation time of PM2.5 sensors while maintaining a high calibration performance.
Publications
- Sonu Kumar Jha, Mohit Kumar, Vipul Arora, Sachchida Nand Tripathi, Vidyanand Motiram Motghare, and A. A. Shingare, “Domain adaptation based deep calibration of low-cost PM2.5 sensors”, IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021.
- Kalpit Yadav, Vipul Arora, Sonu Kumar Jha, Mohit Kumar, and Sachchida Nand Tripathi. Few-shot calibration of low-cost air pollution (pm2.5) sensors using meta-learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.00640, 2021.
- Swapnil Dey, Vipul Arora, and Sachchida Nand Tripathi, “Leveraging unsupervised data and domain adaptation for deep regression in low-cost sensor calibration”, IEEE Trans. Neural Networks and Learning Systems.

